The terms user interface (UI), user experience (UX) and usability are linked, but have different focuses. Here are the basic differences:
- User Interface (UI):
- The UI refers to the visual elements and interaction options that a user sees directly on a screen and uses in the app or website. This includes layouts, colors, fonts, images, buttons, icons and other graphic elements, but also branding and trust elements and interaction design.
- The main goal of user interface design is to create an appealing, effective and intuitive user interface that facilitates interaction between the user and the digital product.
- User Experience (UX):
- UX encompasses the entire experience a user has with a product. It refers not only to the visual design (UI), but also to the totality of user interactions, emotions, expectations and perceptions during the entire process of the user experience - this also includes the perceptions before and after the actual use.
- The main goal of UX is to ensure that the product meets the needs and expectations of the user and provides a positive, satisfying and efficient experience - avoiding frustration at every point of the customer journey.
- Usability:
- Usability refers to the ease of use of a product and how easily users can perform certain tasks on the website or in the application.
- It focuses on the efficiency, effectiveness and satisfaction of users when using the product. Predictability is also part of usability, that users find familiar patterns (search is at the top or top right), navigation is at the top or left and so on.
- Usability is a sub-aspect of the overall UX , and precisely the area that happens during use by the user. A user-friendly UI is an important part of usability.
The temporal aspect in particular is worth noting. The user experience starts even before the user uses the product, with the user's ideas, expectations and also pre-judgements. The user experience then runs through the process of use - usability maps this temporal aspect with the satisfaction, effectiveness and efficiency of use. And finally, the user experience concludes with the experiences made and emotional connections after use.
While user interface design is mainly concerned with fonts, colors, buttons, images, icons, etc., user experience design takes a broader view: The UX designer considers the target groups and personas, defines the information architecture, works with wireframes and prototypes, designs interaction paths along the customer journey and develops scenarios and interaction elements. Even storytelling is part of the user experience.
For example, the UX designer creates a clickable wireframe concept as an early prototype to visualize the information architecture and interaction paths:
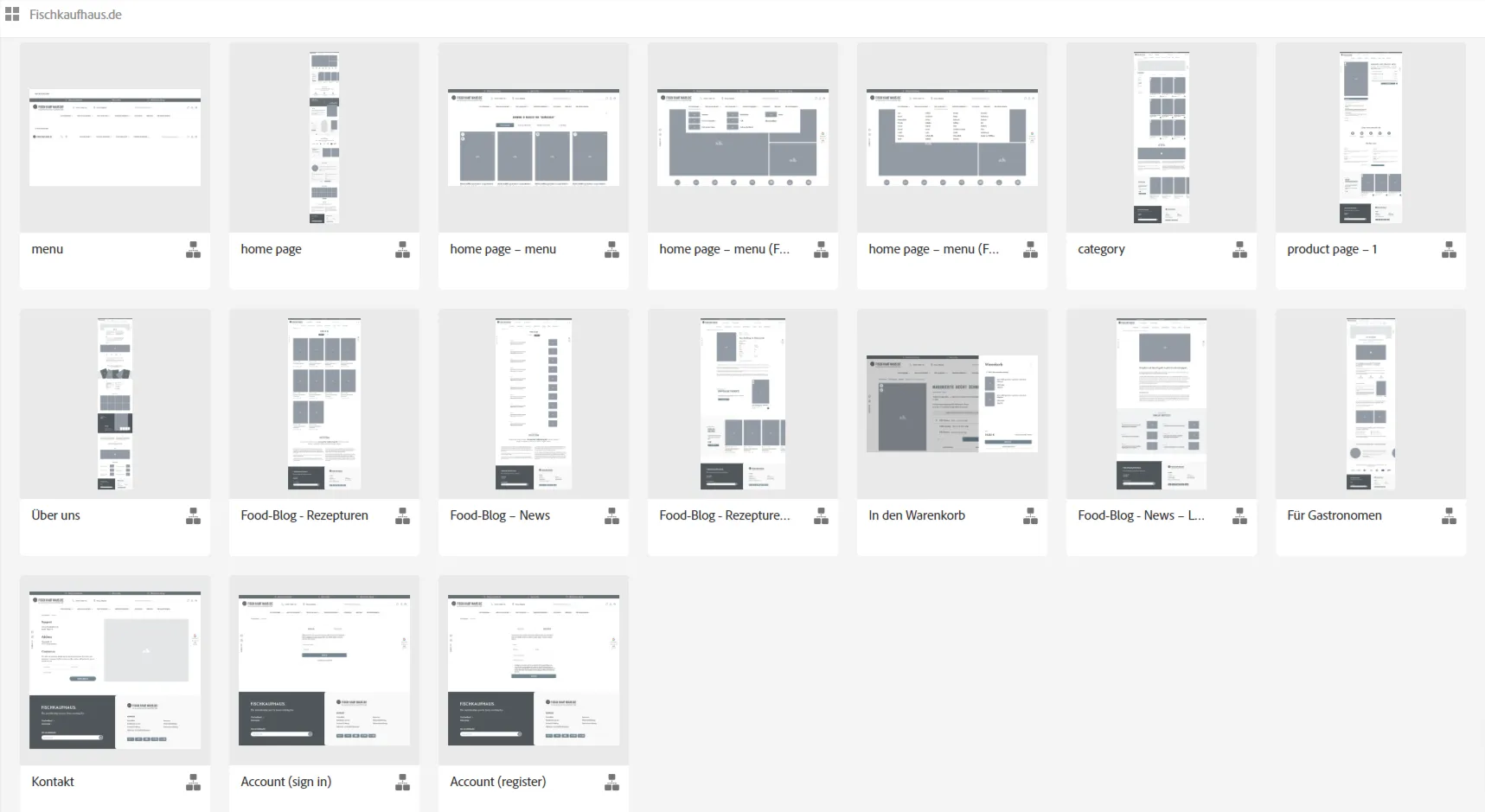
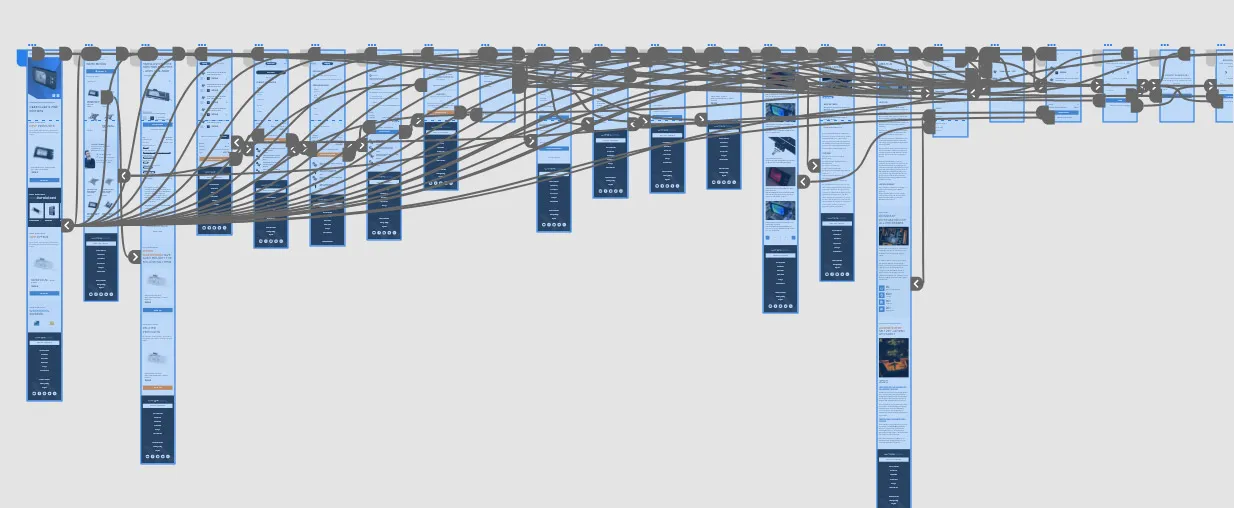
Here is once example of a mobile user interface design with the click paths created using Adobe XD:
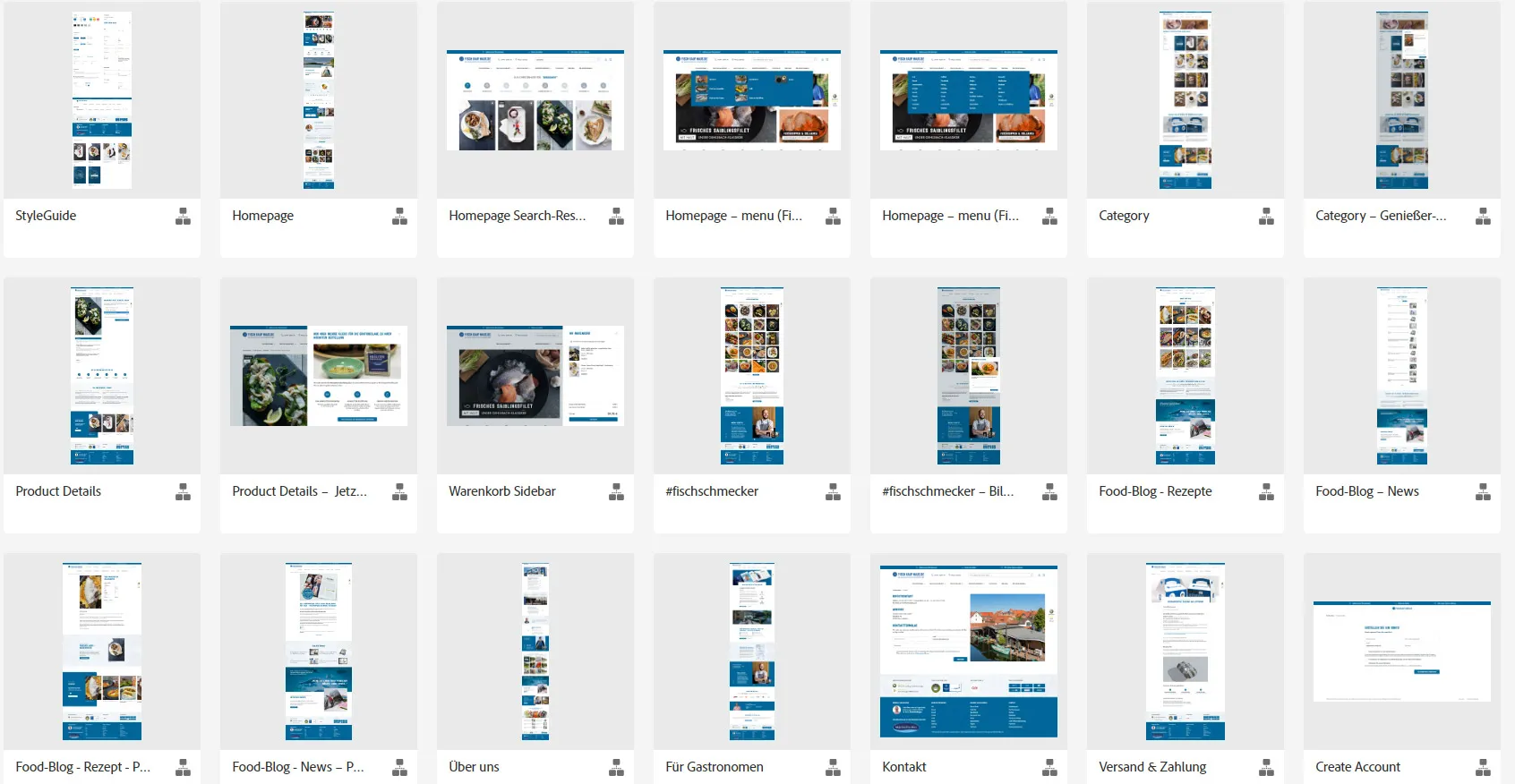
The actual design of the sections of a website then affects the user interface. Here is an example of the user interface design from the wireframe concept above:
In summary: UI is focused on the visual design and interaction elements , UX refers to the overall experience of the user, and usability focuses on the ease and ease of use of a product. All three aspects are important in creating a digital product that is both aesthetically pleasing and functional, providing a positive user experience while reducing any potential for frustration.
User experience vs. user interface vs. usability: know the differences
From Matthias Petri
